
Alphabetical Index
Browse by Elements
Keyword Search
Dry Etchants
Dry and Wet Etchants
Wet Etchants
Bulk Etchants
Layer Etchants
Nano Etchants
Single Crystal Etchants
Thin Film Etchants
Thin Foil Etchants
Wafer Etchants
Al Etchants
Cd Etchants
Ga Etchants
Ge Etchants
In Etchants
New Etchants
Other Etchants
Si Etchants
Zn Etchants
Help
Home
Examples of Defect Adders Within the Oxide-Masked Al Etching Process Sequence
Material Name: Aluminium
Record No.: 41
Primary Chemical Element in Material: Al
Sample Type: Layer
Uses: Etching
Etchant Name: None
Etching Method: Dry etching
Etchant (Electrolyte) Composition: No data
Procedure (Condition): No data
Note: As illustrated in Figure 1, the defect types, referred
to as “post hard-mask etch residue,” “post metal etch
residue,” “blocked etch metal island,” “particle,” “bridging,”
“particulate bridging,” and “corrosion,” were found at the
early stage of development. Interestingly, the major adders of post hard-mask etch residue, post metal etch residue, and
blocked etchmetal island were particularly high in the oxidemasked
Al patterning but few in the conventional resistmasked
Al patterning. From the observations of scanning
electron micrographs as shown in Figure 1, these three defect
types pose a tangible and substantial yield risk due to their
subtle physical characteristics and high density on wafer.
Hence, it is important to understand the behavior of these
defect adders within the Al etching process sequence.
Reference: Hong-Ji Lee, Che-Lun Hung, Chia-Hao Leng, Nan-Tzu Lian, Ling-Wu Young,
Tahone Yang, Kuang-Chao Chen, and Chih-Yuan Lu, Etch Defect Characterization and Reduction in
Hard-Mask-Based Al Interconnect Etching, International Journal of Plasma Science and Engineering, Volume 2008, Article ID 154035, pp. 1-5.
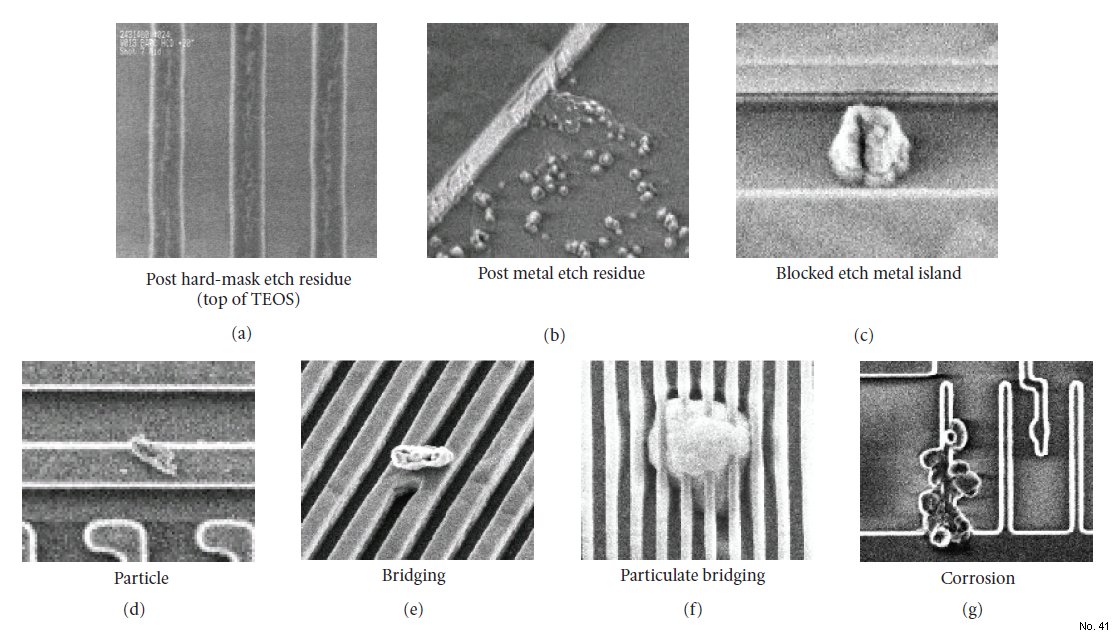
Figure 1: Examples of defect adders within the oxide-masked Al etching process sequence.