
Alphabetical Index
Browse by Elements
Keyword Search
Dry Etchants
Dry and Wet Etchants
Wet Etchants
Bulk Etchants
Layer Etchants
Nano Etchants
Single Crystal Etchants
Thin Film Etchants
Thin Foil Etchants
Wafer Etchants
Al Etchants
Cd Etchants
Ga Etchants
Ge Etchants
In Etchants
New Etchants
Other Etchants
Si Etchants
Zn Etchants
Help
Home
Plastic and Brittle Fracture Scratches
Material Name: No data
Record No.: 50
Primary Chemical Element in Material: No data
Sample Type: Wafer
Uses: Polishing
Etchant Name: None
Etching Method: Polishing
Etchant (Electrolyte) Composition: No data
Procedure (Condition): No data
Note: Ring et al. reviewed the mechanical properties and fracture mechanics of materials in order to understand the surface damage caused during
CMP. The resulting failure was predicted by various
mechanical wear (or scratching) equations depending
upon the assumption of plastic deformation or brittle
fracture (Fig. 1). The wear rate goes from reasonably
low rates for plastic wear to rates with higher orders of
magnitude for brittle fracture.
Reference: Tae-Young KWON, Manivannan RAMACHANDRAN, Jin-Goo PARK, Scratch formation and its mechanism in chemical mechanical
planarization (CMP), Friction 1(4): 279–305 (2013).
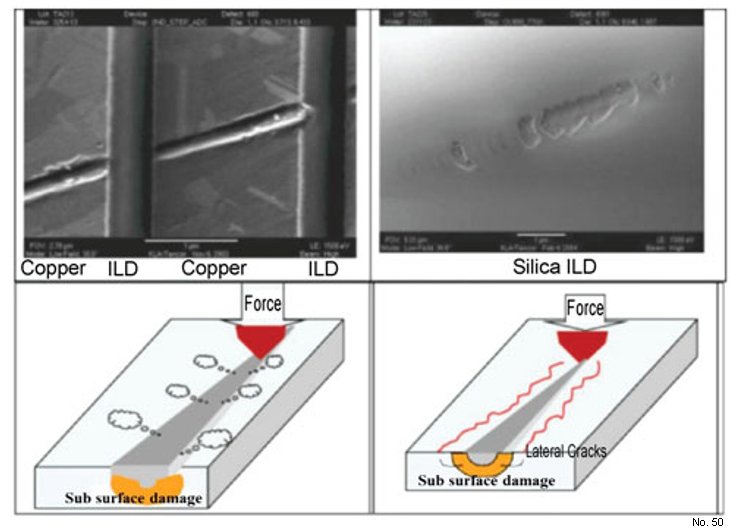
Figure 1: Schematic of (a) plastic deformation and (b) brittle
fracture.