
Alphabetical Index
Browse by Elements
Keyword Search
Dry Etchants
Dry and Wet Etchants
Wet Etchants
Bulk Etchants
Layer Etchants
Nano Etchants
Single Crystal Etchants
Thin Film Etchants
Thin Foil Etchants
Wafer Etchants
Al Etchants
Cd Etchants
Ga Etchants
Ge Etchants
In Etchants
New Etchants
Other Etchants
Si Etchants
Zn Etchants
Help
Home
Low Sample Temperature
Material Name: Silicon
Record No.: 95
Primary Chemical Element in Material: Si
Sample Type: Wafer
Uses: Etching
Etchant Name: None
Etching Method: Dry etching
Etchant (Electrolyte) Composition: No data
Procedure (Condition): No data
Note: No data
Reference: Burkhard E. Volland, Profile simulations of gas chopping etching
processes, PhD Thesis, Institute of Physics, University of Kassel, 2004, p. 39.
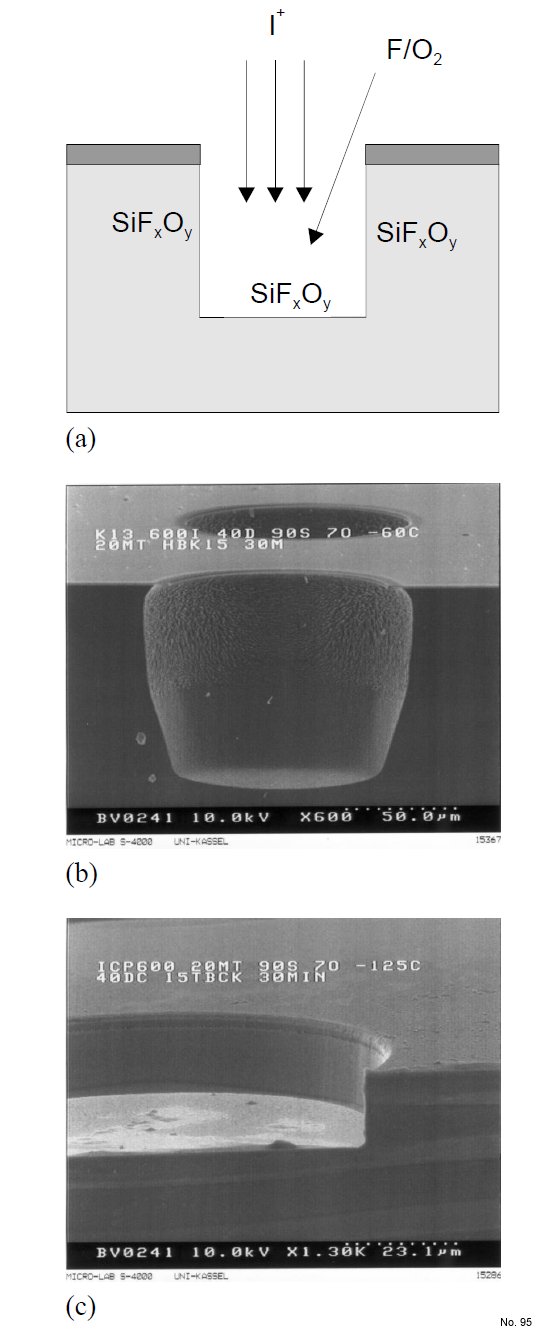
Figure 1: Anisotropy caused by
low sample temperature. Due to the
low sample temperature, the spontaneous
etching of fluorine with silicon
reduces dramatically. This effect is
enhanced by the addition of oxygen
to the process gas mixture (a). Etching
proceeds only due to ion bombardment
(ion-enhanced etching). Because
of the direct flow of ions, etching
proceeds only at the bottom, not at
the sidewalls (a). Samples have been
etched in an ICP reactor (Oxford Instruments
Plasma Technology System
100) with a 90 sccm SF6/9 sccm O2
process gas mixture, 20 mTorr operating
pressure, 60 W ICP power, 40 V dc
bias, and a helium backing of 15 Torr,
at -60 C (b) or -125 C (c). The vertical
etching rate reduces from 3 µm/min
(b) to 0.5 µm/min (c) as the sample
temperature decreases from -60 C to -
125 C, but the anisotropy of the profile
increases with decreasing sample
temperature. The sample etched at -
60 C (b) still suffers considerable lateral
etching due to the spontaneous
etching reaction of fluorine with silicon,
which vanishes at a sample temperature
of -125 C (c).