
Alphabetical Index
Chemical Composition
Keyword Search
Named Inclusions
Steel Index
Exogenous Inclusions
Indigenous Inclusions
Macro Inclusions
Micro Inclusions
Nano Inclusions
Iron Oxide Inclusions
Nitride Inclusions
Oxide Inclusions
Phosphide Inclusions
Silicate Inclusions
Spinel Inclusions
Sulfide Inclusions
Refractory Inclusions
Slag Inclusions
Figure Browser
Help
Contact Us
Home
Thermal stresses near nonmetallic inclusions and wear parts near nonmetallic inclusion in wheel steel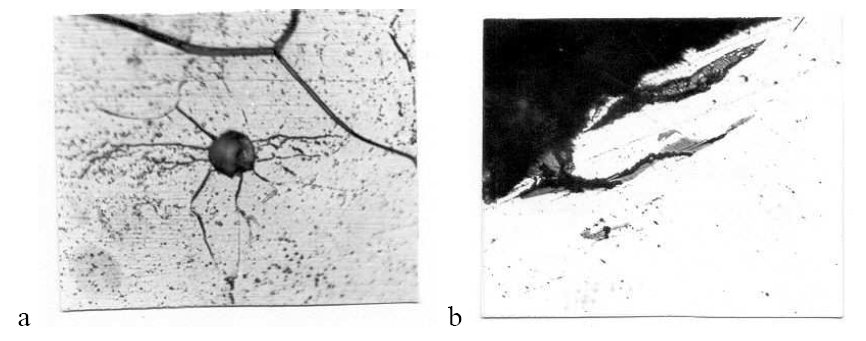
Figure 1: Thermal stresses near nonmetallic inclusions (a) and wear parts near nonmetallic inclusion (b), Mag. 600 X.
Inclusion name: Inclusion
Record No.: 856
Inclusion formula: No data
Inclusion type (Macro/Micro/Nano): No data
Inclusion type (Exogenous/Indigenous): No data
Inclusion classification: No data
Inclusion composition in weight %: No data
Sample: Wheel steel
Steel composition in weight %: No data
Note: It is well known that formation of defects of many types during railway wheels service somehow or other is connected to nonmetallic inclusions in wheel steel. Microbreakes connected with nonmetallic inclusions have different origin. The first one is “deformational”, the second is “thermal” and the third is “hydrogenous”. The objective of this work is the study of nature of microbreaking in wheel steel relative to nonmetallics. Mechanisms of microbreaking of all types near different nonmetallics had been investigated and their influence on safety threshold of railway wheels had been analyzed herein.
Thermal microbreaks (voids or ductile cracks) are generated either during steel cooling after hot deformation of wheel steel or wheel cooling during thermal hardening. This phenomenon is associated with difference in thermal compression coefficient between inclusion and matrix that generates thermal stresses near nonmetallic inclusions (Fig. 1a). The same factor is significant during formation of thermal stress fatigue and, as consequence, microbreaking of wheel in service thermal cyclic loads.
Plastic shifts near tread surface are developing during wheel service and if inclusions are located in this area they cause cracks and wear parts formation. These are also microbreaks of deformational origin. Ready to use wheels inherit inclusions distribution from ingot. During service life wheels are running in severe loading conditions, undertaking alternating loads, subjecting to impacts from higher or lower and frequently cyclic changing temperatures. Reliability and durability of railway wheel are connected with its resistance for cracking incipiency and development. Near inclusions, in conditions of alternating, cyclic and constant loads and temperatures, local stresses field occurs inevitably, and its magnitude depends on the type of loading, size and form as well as inclusions interference. For example, under cycling loading, stresses near inclusions reach the value of steel yield stress. Process of accumulation of such stresses causes the incipiency of cracks fatigue near inclusions (Fig. 1b).
Additional links: Not shown in this demo version.
Reference: Not shown in this demo version.