
Alphabetical Index
Chemical Composition
Keyword Search
Named Inclusions
Steel Index
Exogenous Inclusions
Indigenous Inclusions
Macro Inclusions
Micro Inclusions
Nano Inclusions
Iron Oxide Inclusions
Nitride Inclusions
Oxide Inclusions
Phosphide Inclusions
Silicate Inclusions
Spinel Inclusions
Sulfide Inclusions
Refractory Inclusions
Slag Inclusions
Figure Browser
Help
Contact Us
Home
Cristobalite
Chemical formula: SiO2
Modifications: Several silica modifications are known. The following phases are stable at ordinary pressure: quartz - high quartz - tridymite - cristobalite - melt.
Melting point (high cristobalite): 1723oC
Stability range (high cristobalite): 1470-1723oC
Transformation point (high-low cristobalite): 180-270oC
Density: 2.23 (high), 2.32-2.38 (low) g/cm3
Microhardnes: cca 1600 kp/mm2 (low)
Hardness (Moh's): 6-7
Luminescence: Cristobalite often shows a light-blue fluorescence in EPMA.
Colour in air, bright field reflection: Milk white (beta-cristobalite)
Colour, polarized reflection: No data
Shape: No data
Crystal system: Tetragonal, pseudocubic
Cell dimensions: a=4.9709 A, c=6.9278 A
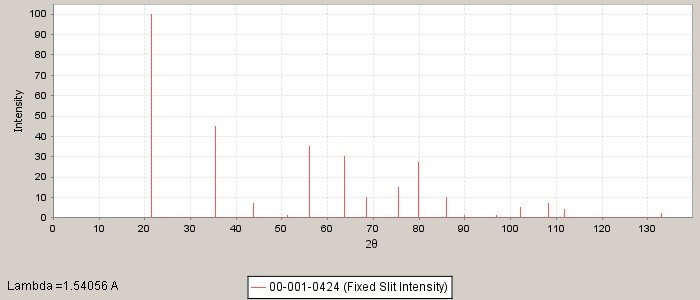
PDF number: 00-001-0424
ICSD number: 024587
Note: In non-metallic steel inclusions cristobalite often crystalizes as dendrites in a glassy ot crystallized matrix of various metal silicates. The polished microsections of these dendrites often aooear as rosettes. Cristobalite also occurs as a scale around the inclusions and lining the inside of the blowholes which are often visible in silicate inclusions.