
Alphabetical Index
Chemical Composition of Steels
Keyword Search
Steel Names
Alloyed Steels
Carbon Steels
Cast Irons
Chromium Steels
Cold Work Tool Steels
Creep Resistant Steels
Hot Work Tool Steels
Molybdenum Steels
PM steels
Stainless Steels
Structural Steels
Tool Steels
Vanadium Steels
White Cast Irons
M2C Carbides
M3C Carbides
M7C3 Carbides
M23C6 Carbides
MC Carbides
Light Microscopy
EDS/WDS Microanalysis
Scanning Electron Microscopy
Transmission Electron Microscopy
X-Ray Diffraction
Help
Contact Us
Home
Carbide Extraction From the Stabilised Austenitic Cast Steel
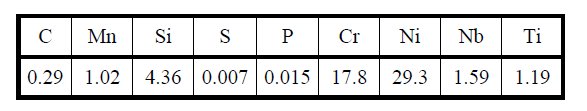
Table 1: Chemical composition of the tested alloy, wt%.
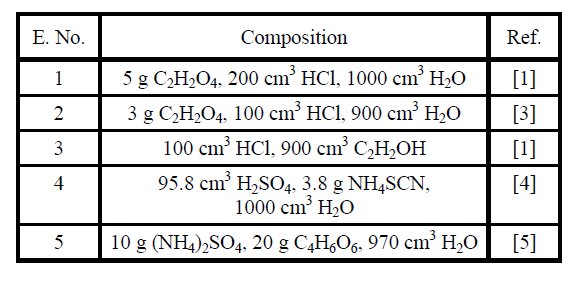
Table 2: Chemical composition of electrolyte (E) solutions.
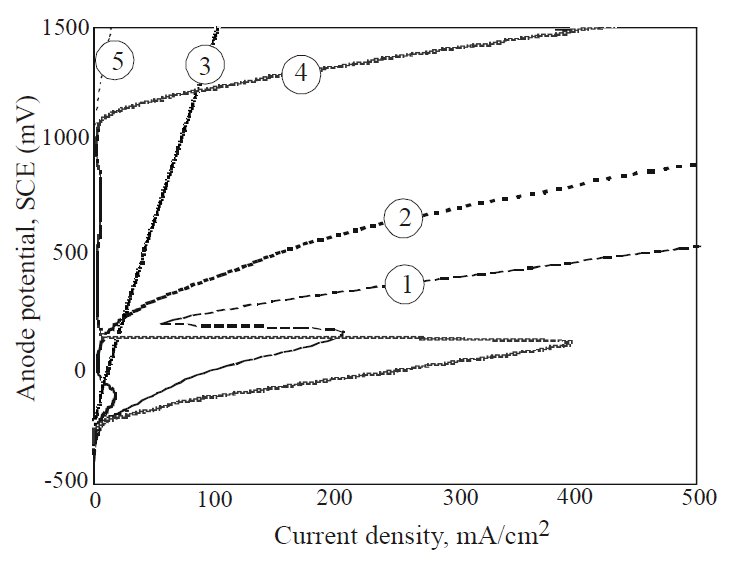
Figure 1: Anodic polarization curves in tested electrolytes presented in Table 2.
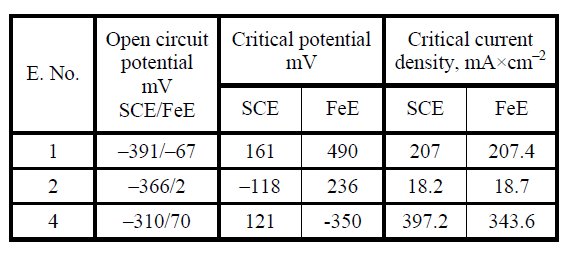
Table 3: Electrochemical parameters in electrolytes.
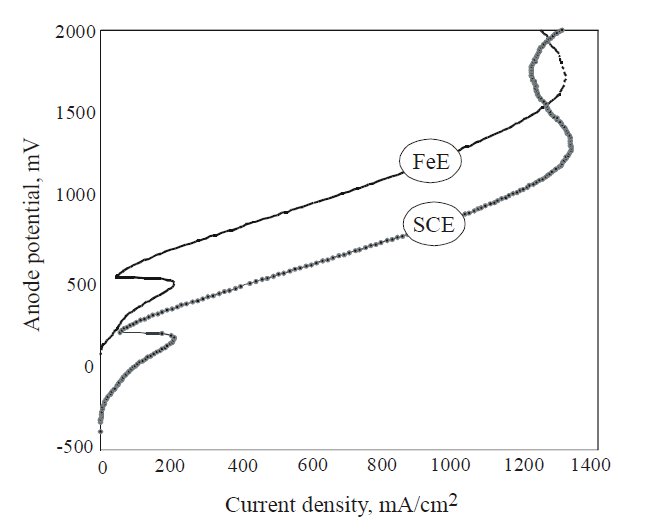
Figure 2: Anodic polarization curves in electrolyte No.1, relative to SCE – standard calomel electrode, and to FeE – ferrous electrode.
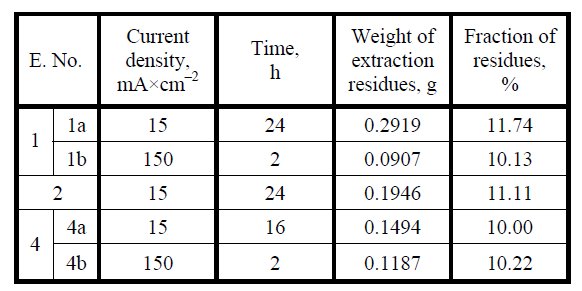
Table 4: Conditions and results of selective dissolution.
The studies were made on samples of dimensions 10 × 30 mm, prepared from the creep-resistant 30% Ni –18% Cr cast steel with additions of niobium and titanium (Table 1).
Basing on the data published in literature, it was decided to use in the investigation electrolytes of the chemical compositions given in Table 2.
To determine the conditions under which the processes of an electrolytic extraction should be conducted, the curves of anodic polarisation were plotted for all the electrolytes, using an ATLAS 9431 potentiostat.
Adequately prepared cast steel samples were immer-sed in an electrolyte solution at a temperature of 25 °C, mixed with a magnetic stirrer. Having determined the stationary potential characteristics of each measurement, the polarisation was made within a range of the values from stationary potential up to 2000 mV. The readout density was 10 mV with the potential changing at a rate of 10 mV/s. Calomel electrode was used as a reference material. The curves of anodic polarisation plotted for the examined cast steel in individual solutions of electrolytes are shown in Figure 1.
An analysis of the plotted curves indicates that in the case of solutions No's. 1, 2 and 4 it has been possible to match the electrochemical conditions in a way such as to make the austenitic matrix digest completely, leaving in an isolate the phase constituents typical of cast steel. On the contrary, in solutions nos. 3 and 5, within the investigated range of the current voltage values, no clearly marked areas of an active and passive state have been observed to exist (the process of austenite digestion did not take place).
In the process of cast steel digestion it has been decided to use a cathode made of an acid-resistant steel sheet and, to check the current parameters, anodic polarisation was carried out in respect of this electrode. Figure 2 shows an example of the polarisation curves of cast steel in electrolyte No. 1 in respect of the calomel electrode (SCE) and steel electrode (FeE). In all electrolytes, the polarisation curves were shifted upwards in respect of the steel electrode by a constant value of the anodic potential, with critical current density value remaining the same. The values of the critical currents read out from the plotted curves and the corresponding anodic potentials in the examined electrolytes are compiled in Table 3. Basing on the collected data, the parameters of the electrolysis were selected and used next for the extraction – Table 4. To prove how significant is the effect of the current density on the volume of the isolate, specially in the case when the alloy includes a small amount of the fine-dispersed phases [3], it has been decided to use in the case of electrolytes No. 1 and 4 the current of both low (electrolytes No. 1 a and 4 a) as well as high (electrolytes nos. 1 b and 4 b) density.
All the processes of extraction were conducted in a similar way. The samples, after having been thoroughly cleaned and dried, were weighed at an accuracy of up to ±0.1 mg. The sediment obtained from this operation was thoroughly rinsed with ethyl alcohol, spinned and dried at a temperature of 70 °C. The rinsed and dried sample residue and the isolate were weighed once again. From the weighed fractions the percent content of the isolates was calculated.
Every process was repeated three times. The differences in a volume of the isolates obtained from the secondary isolations did not exceed 7 %. The mean values (in %) calculated from the volume of the obtained isolates are compiled in Table 4.
Reference: Renata CHYLINSKA, Malgorzata GARBIAK, Bogdan PIEKARSKI, Electrolytic Phase Extraction in Stabilised Austenitic Cast Steel, MATERIALS SCIENCE (MEDŽIAGOTYRA). Vol. 11, No. 4, 2005, pp. 348-349.